Adrenochrome - Wikipedia
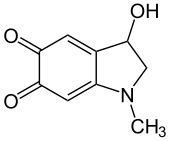
Adrenochrome is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C9H9NO3 produced by the oxidation of adrenaline (epinephrine). The derivative carbazochrome is a hemostatic medication. Despite a similarity in chemical names, it is unrelated to chrome or chromium.
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-Hydroxy-1-methyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indole-5,6-dione | |
| Other names
Adraxone; Pink adrenaline | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.176 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C 9H 9N O 3 | |
| Molar mass | 179.175 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 3.264 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 115–120 °C (239–248 °F; 388–393 K) (decomposes) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state(at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
 N verify (what is N verify (what is  Y Y  N ?) N ?)
| |
| Infobox references | |
Chemistry Edit
In vivo, adrenochrome is synthesized by the oxidation of epinephrine. In vitro, silver oxide (Ag2O) is used as an oxidizing agent.[1] Its presence is detected in solution by a pink color. The color turns brown upon polymerization.
Effect on the brain Edit
Several small-scale studies (involving 15 or fewer test subjects) conducted in the 1950s and 1960s reported that adrenochrome triggered psychotic reactions such as thought disorder, derealization, and euphoria.[2] Researchers Abram Hoffer and Humphry Osmond claimed that adrenochrome is a neurotoxic, psychotomimetic substance and may play a role in schizophrenia and other mental illnesses.[3] In what they called the "adrenochrome hypothesis",[4] they speculated that megadoses of vitamin C and niacin could cure schizophrenia by reducing brain adrenochrome.[5][6] While the treatment of schizophrenia with such potent anti-oxidants is highly contested in literature, and adrenochrome is not currently believed to have any psychedelic properties,[7] a number of recently published papers consider Hoffer's paper a landmark contribution to the notion that impairment of what's now termed the anti-oxidant defense system (AODS) seems to play a role in schizophrenia.[8]
Legal status Edit
Adrenochrome is unscheduled by the Controlled Substances Act in the United States. It is not an approved drug product by the Food and Drug Administration, and if produced as a dietary supplement it must comply with Good manufacturing practice.[9]
In popular culture Edit
- Author Hunter S. Thompson mentioned adrenochrome in his book Fear and Loathing in Las Vegas. The adrenochrome scene also appears in the novel's film adaptation. In the DVD commentary, director Terry Gilliam admits that his and Thompson's portrayal is a fictional exaggeration. In fact, Gilliam insists that the drug is entirely fictional and seems unaware of the existence of a substance with even a similar name. Hunter S. Thompson also mentions adrenochrome in his book Fear and Loathing on the Campaign Trail '72. In the footnotes in chapter April, page 140 he says, "It was sometime after midnight in a ratty hotel room and my memory of the conversation is haze, due to massive ingestion of booze, fatback, and forty cc's of adrenochrome."
- The harvesting of an adrenal gland from a live victim to obtain adrenochrome for drug abuse is a plot feature in the first episode "Whom the Gods would Destroy", of Series 1 of the British TV series Lewis (2008).[10]
- In Anthony Burgess' 1962 novel A Clockwork Orange, "drencrom" (presumably the Nadsat term for adrenochrome) is listed as one of the potential drugs that can be added to Moloko Plus (milk laced with a drug of the consumer's choice) at the Korova Milk Bar.
- In Fear The Walking Dead season 3 episode 14, "During the show, Nick and Troy took a very strange drug. It was described as an actual human brain stem that contained chemicals from the adrenal gland."[11]
- Adrenochrome is also featured in a variety of conspiracy theories, such as QAnon and Pizzagate.[12]
References Edit
- ^ MacCarthy, Chim, Ind. Paris 55,435(1946)
- ^ Smythies J (March 2002). "The adrenochrome hypothesis of schizophrenia revisited". Neurotoxicity Research. 4 (2): 147–50. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.688.3796 . doi:10.1080/10298420290015827. PMID 12829415.
- ^ Hoffer A, Osmond H, Smithies J (January 1954). "Schizophrenia; a new approach. II. Result of a year's research". The Journal of Mental Science. 100 (418): 29–45. doi:10.1192/bjp.100.418.29. PMID 13152519.
- ^ Hoffer A (1999). "The Adrenochrome Hypothesis and Psychiatry". The Journal of Orthomolecular Medicine. 14 (1): 49–62.
- ^ Hoffer A, Osmond H (1967). The Hallucinogens. Academic Press. ISBN 978-1-4832-6169-0.
- ^ Hoffer A (1994). "Schizophrenia: An Evolutionary Defense Against Severe Stress" (PDF) . Journal of Orthomolecular Medicine. 9 (4): 205–221.
- ^ "The controversy that these reports created just sort of died away, and the adrenochrome family has never been accepted as being psychedelic. No one in the scientific community today is looking in and about the area, and at present this is considered as an interesting historical footnote." As seen at: Shulgin A, Shulgin A (1991). "#157 (TMA)". PiHKAL - A Chemical Love Story. Transform Press.
- ^ Yao JK, Reddy R (October 2011). "Oxidative stress in schizophrenia: pathogenetic and therapeutic implications". Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 15 (7): 1999–2002. doi:10.1089/ars.2010.3646. PMC 3159103 . PMID 21194354.
- ^ "Compound summary for adrenochrome". National Center for Biotechnology Information, PubChem Database . Retrieved 2020-01-22 .
- ^ "Inspector Lewis Series Synopsis". Archived from the original on 2008-06-26.
- ^ Stephanie Dube Dwilson (October 9, 2017). " ' Fear the Walking Dead': Was Nick's Adrenal Brain Stem Drug Real?". Heavy.com.
- ^ Alex Nichols (June 6, 2019). "Slender Man for Boomers". The Outline. Retrieved 16 March 2020.
External links Edit
- Adrenochrome Commentary at erowid.org
- Adrenochrome deposits resulting from the use of epinephrine-containing eye drops used to treat glaucoma from the Iowa Eye Atlas (searched for diagnosis = adrenochrome)